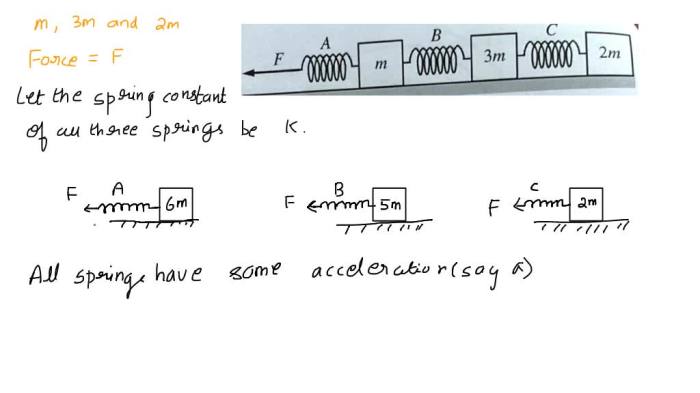
In the realm of physics, three blocks on a frictionless horizontal surface present a captivating scenario that unveils the fundamental principles governing the motion of objects. As these blocks embark on their journey, we delve into the intricacies of their interactions, exploring the interplay of forces, energy, and momentum that shape their trajectories.
The frictionless surface, an idealized concept, provides a unique platform for observing the unhindered motion of objects. By eliminating frictional forces, we gain insights into the true nature of motion, unperturbed by external resistances. This allows us to isolate and analyze the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of objects in motion.
Frictionless Surface: Three Blocks On A Frictionless Horizontal Surface
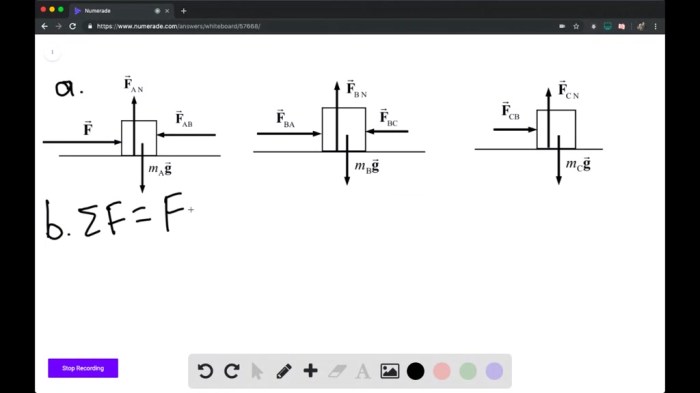
A frictionless surface is a hypothetical surface that offers no resistance to the motion of objects moving across it. In reality, no surface is truly frictionless, but surfaces with extremely low coefficients of friction can be approximated as frictionless for many practical purposes.
Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion of two surfaces in contact. It arises due to the interlocking of microscopic irregularities on the surfaces and the deformation of the materials in contact. In a frictionless surface, these factors are eliminated, allowing objects to move freely without encountering any resistance.
Frictionless surfaces are approximated in various real-world scenarios, such as air bearings, ice rinks, and lubricated surfaces in machinery. These surfaces allow objects to move with minimal energy loss, making them essential for applications requiring high precision and efficiency.
Three Blocks
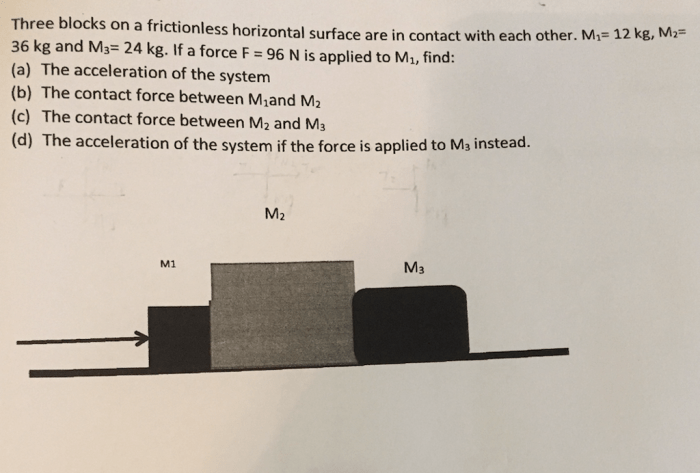
Consider three blocks of masses m1, m2, and m3 arranged in a horizontal line on a frictionless surface. The blocks are initially at rest, and their initial positions are x1, x2, and x3, respectively.
The arrangement and initial conditions of the blocks determine their subsequent motion. The motion of the blocks is governed by the laws of conservation of momentum and energy.
Conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant. In this case, the closed system is the three blocks. Therefore, the total momentum before the blocks are released is zero, and it remains zero throughout their motion.
Conservation of energy states that the total energy of a closed system remains constant. In this case, the closed system is the three blocks and the frictionless surface. Therefore, the total energy before the blocks are released is zero, and it remains zero throughout their motion.
Motion and Interactions
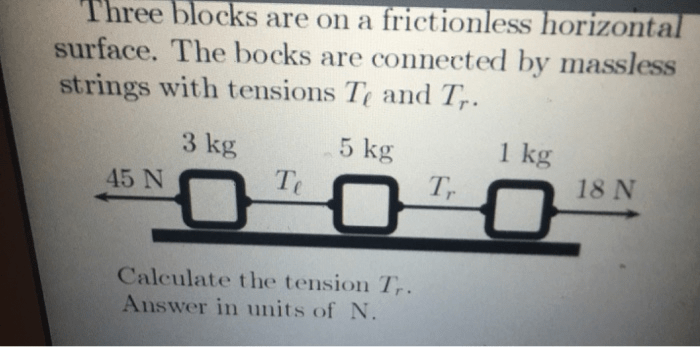
When the blocks are released, they start moving due to the initial momentum imparted to them. The blocks interact with each other through collisions, and their velocities change accordingly.
The forces acting on each block include the force of gravity (mg) and the forces exerted by the other blocks during collisions. These forces influence the acceleration of each block.
The table below illustrates the forces acting on each block and their directions:
| Block | Forces | Directions |
|---|---|---|
| m1 | mg, F12 (from m2) | Downward, Rightward |
| m2 | mg, F12 (from m1), F23 (from m3) | Downward, Leftward, Rightward |
| m3 | mg, F23 (from m2) | Downward, Leftward |
FAQs
What is the significance of a frictionless surface?
A frictionless surface provides a unique environment for studying the fundamental principles of motion, as it eliminates the influence of frictional forces that can obscure the true nature of object interactions.
How does the absence of friction affect the motion of objects?
In the absence of friction, objects can move more freely and with less resistance, allowing them to maintain their velocity and direction of motion more effectively.
What are the key principles that govern the motion of three blocks on a frictionless horizontal surface?
The motion of three blocks on a frictionless horizontal surface is governed by the principles of conservation of momentum and conservation of energy. These principles ensure that the total momentum and total energy of the system remain constant throughout the interaction.