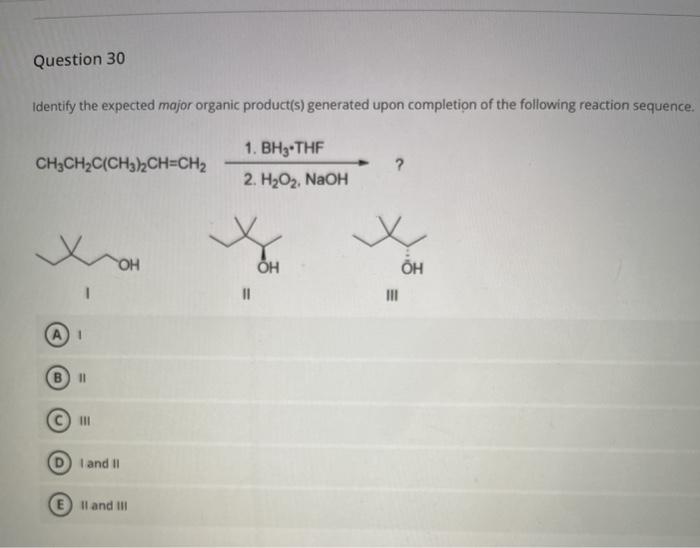
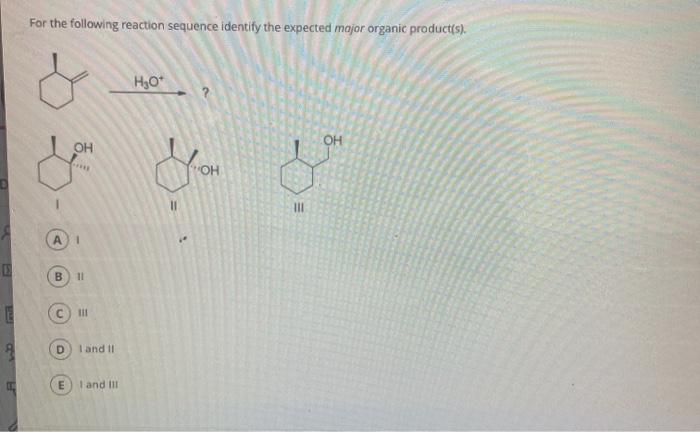
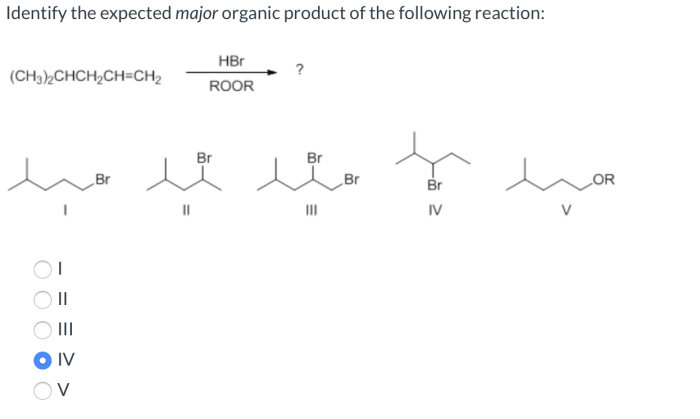
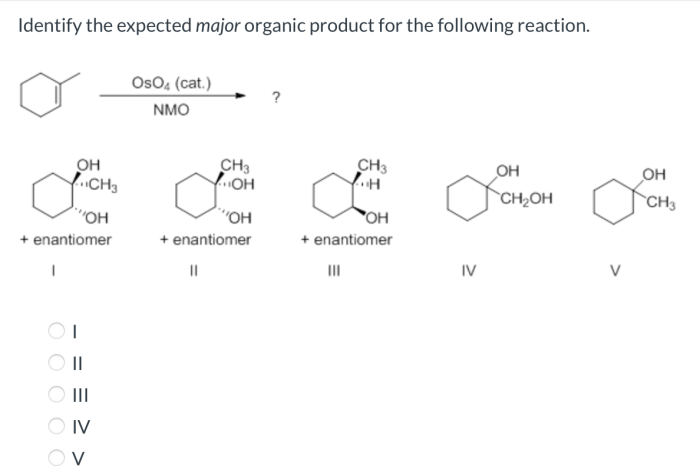
Identify the expected major organic product of the following reaction – In the realm of organic chemistry, identifying the expected major organic product of a reaction is a fundamental skill. It involves understanding the interplay of functional groups, reaction mechanisms, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of these concepts, empowering you to predict the outcome of organic reactions with precision.
Delving into the intricacies of organic reactions, we will explore the various types of reaction mechanisms and how they influence the formation of products. Regioselectivity and stereoselectivity will be examined, shedding light on the factors that govern the regiochemical and stereochemical outcomes of reactions.
Identifying Functional Groups
Identifying functional groups is crucial in organic reactions as they determine the reactivity and properties of organic compounds. Common functional groups include alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines. Understanding their structures and reactivities helps predict the outcome of organic reactions.
Reaction Mechanisms
Reaction mechanisms describe the step-by-step process of organic reactions. They help predict the products and intermediates formed. Common mechanisms include nucleophilic substitution, electrophilic addition, and radical reactions. Understanding reaction mechanisms enables chemists to design and optimize synthetic strategies.
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity
Regioselectivity refers to the preferential formation of one product over others based on the regiochemistry of the reaction. Stereoselectivity refers to the preferential formation of one stereoisomer over others based on the stereochemistry of the reaction. Factors influencing regioselectivity and stereoselectivity include the nature of the reactants, reaction conditions, and catalysts.
Major and Minor Products
In many organic reactions, a mixture of products is formed. The major product is the one formed in the highest yield, while the minor product is formed in a lower yield. Factors determining the formation of major and minor products include the stability of the products, the reaction conditions, and the regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction.
Reaction Conditions, Identify the expected major organic product of the following reaction
Reaction conditions, such as temperature, solvent, and catalysts, play a crucial role in organic reactions. Temperature affects the rate and equilibrium of the reaction. Solvents can influence the solubility and reactivity of the reactants and products. Catalysts can accelerate the reaction rate without being consumed.
Multi-Step Synthesis
Multi-step synthesis involves a series of consecutive reactions to obtain the desired product. It allows for the construction of complex molecules from simpler starting materials. Strategies for designing multi-step synthesis routes include retrosynthesis, functional group interconversion, and protecting group chemistry.
Reaction Tables
Reaction tables provide a concise summary of key information for a given organic reaction, including reactants, products, reaction conditions, and yield. They help compare different reactions and optimize reaction outcomes.
Reaction Mechanisms with Diagrams
Reaction mechanisms can be illustrated using detailed diagrams. These diagrams depict the step-by-step process of the reaction, showing the intermediates, transition states, and electron flow. They provide a visual representation of the reaction mechanism, aiding in understanding the reaction pathway.
Helpful Answers: Identify The Expected Major Organic Product Of The Following Reaction
What is the importance of identifying functional groups in organic reactions?
Functional groups are the reactive centers of organic molecules and play a crucial role in determining their chemical behavior. Identifying functional groups allows chemists to predict the reactivity of molecules and the types of reactions they will undergo.
How do reaction mechanisms help predict the products of a reaction?
Reaction mechanisms provide a step-by-step description of how a reaction occurs. By understanding the mechanism, chemists can identify the intermediates and transition states involved, which helps them predict the products and their relative yields.
What factors influence regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in organic reactions?
Regioselectivity and stereoselectivity are influenced by a combination of factors, including the electronic properties of the reactants, the reaction conditions, and the presence of catalysts. Understanding these factors allows chemists to control the regiochemical and stereochemical outcomes of reactions.