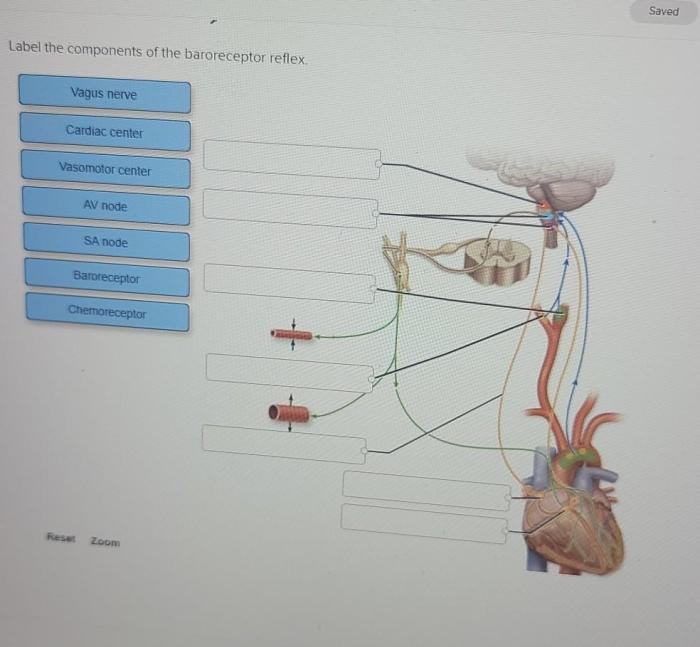
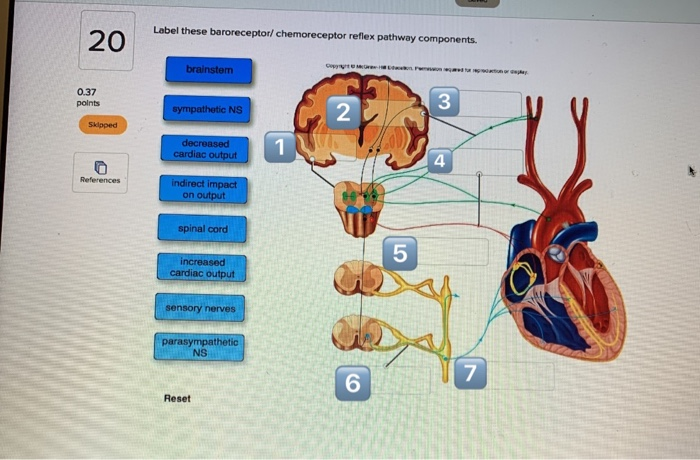
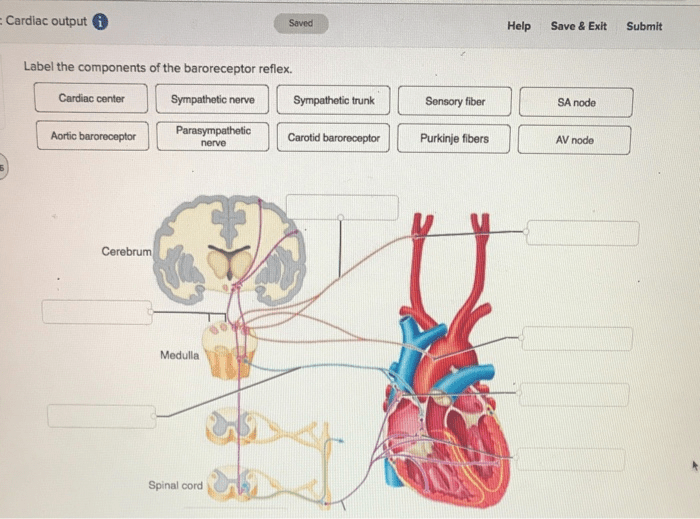
Label the components of the baroreceptor reflex. – Label the components of the baroreceptor reflex is a critical component of the body’s intricate regulatory mechanisms, ensuring the precise maintenance of blood pressure. This reflex pathway, initiated by specialized sensory receptors, plays a pivotal role in detecting and responding to fluctuations in blood pressure, thereby contributing to cardiovascular homeostasis.
Delving into the intricate components of this reflex, we uncover its significance in both health and disease.
Baroreceptors, strategically positioned within the carotid sinus and aortic arch, act as sentinels of the circulatory system, constantly monitoring blood pressure changes. These specialized sensory receptors translate these pressure variations into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the brainstem via afferent nerve fibers.
The glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) and vagus nerve (X) serve as the primary conduits for these signals, relaying the crucial information to the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) within the brainstem.
Baroreceptor Reflex
Baroreceptor reflex merupakan mekanisme fisiologis yang berperan penting dalam mengatur tekanan darah. Refleks ini melibatkan deteksi perubahan tekanan darah oleh reseptor sensorik khusus yang terletak di arteri besar, diikuti oleh aktivasi jalur saraf aferen dan eferen yang mengarah pada respons fisiologis yang sesuai.
1. Sensory Receptors
Baroreseptor adalah reseptor sensorik yang mendeteksi perubahan tekanan darah. Terdapat dua kelompok utama baroreseptor:
- Baroreseptor Sinus Karotis:Terletak di sinus karotis, bagian dari arteri karotis yang terletak di leher.
- Baroreseptor Lengkung Aorta:Terletak di lengkung aorta, bagian dari aorta yang keluar dari jantung.
Baroreseptor adalah ujung saraf yang dimodifikasi yang terbungkus dalam kapsul jaringan ikat. Ketika tekanan darah meningkat, kapsul meregang, merangsang ujung saraf dan menghasilkan potensial aksi.
2. Afferent Pathways, Label the components of the baroreceptor reflex.
Potensial aksi dari baroreseptor ditransmisikan melalui serabut saraf aferen ke batang otak:
- Baroreseptor Sinus Karotis:Aferen melalui saraf glosofaringeal (IX).
- Baroreseptor Lengkung Aorta:Aferen melalui saraf vagus (X).
Serabut saraf aferen ini memasuki nukleus traktus solitarius (NTS) di batang otak.
3. Central Processing
NTS adalah pusat integrasi utama untuk sinyal baroreseptor. Di NTS, sinyal dari baroreseptor diintegrasikan dan respons yang sesuai dihasilkan.
Ketika tekanan darah meningkat, aktivitas baroreseptor meningkat, yang mengarah pada penghambatan aktivitas simpatis dan aktivasi aktivitas parasimpatis.
4. Efferent Pathways
Sinyal eferen dari NTS berjalan melalui jalur berikut:
- Aktivasi Parasimpatis:Melalui saraf vagus, menurunkan detak jantung dan vasodilatasi.
- Penghambatan Simpatis:Melalui pusat vasomotor di medula, menurunkan resistensi perifer.
5. Physiological Responses
Aktivasi refleks baroreseptor menyebabkan respons fisiologis berikut:
- Penurunan denyut jantung (bradikardia)
- Penurunan tekanan darah (hipotensi)
- Vasodilatasi (peningkatan diameter pembuluh darah)
6. Clinical Implications
Refleks baroreseptor sangat penting dalam menjaga homeostasis tekanan darah. Gangguan pada refleks ini dapat menyebabkan masalah kardiovaskular:
- Hipertensi:Disfungsi baroreseptor dapat menyebabkan tekanan darah tinggi.
- Hipotensi:Kerusakan baroreseptor dapat menyebabkan tekanan darah rendah.
FAQ Compilation: Label The Components Of The Baroreceptor Reflex.
What are baroreceptors?
Baroreceptors are specialized sensory receptors that detect changes in blood pressure.
Where are baroreceptors located?
Baroreceptors are located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch.
How do baroreceptors work?
Baroreceptors translate blood pressure changes into electrical signals that are transmitted to the brainstem.
What is the role of the NTS in the baroreceptor reflex?
The NTS integrates baroreceptor signals and generates appropriate responses.
What are the clinical implications of baroreceptor dysfunction?
Baroreceptor dysfunction can contribute to cardiovascular disorders such as hypertension and hypotension.